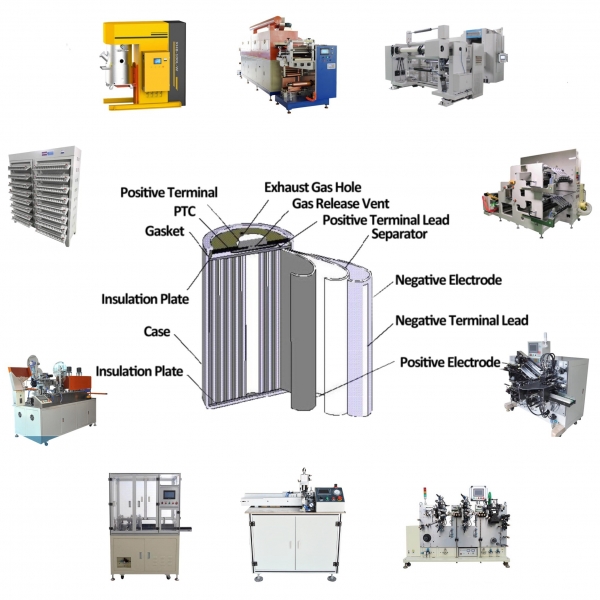
Linea di macchine per la produzione di celle cilindriche automatiche
fabbricazione e attrezzatura del laboratorio della batteria agli ioni di litio 18650
diagramma di flusso delle celle a bottone agli ioni di litio ed elenco delle macchine
fabbricazione e attrezzatura del laboratorio della batteria del sacchetto dello Li-ione
- Posta elettronica : David@tmaxcn.com
- Posta elettronica : Davidtmaxcn@gmail.com
- : No. 39, Xinchang Road, Xinyang, Haicang Dist., Xiamen, Fujian, China (Mainland)
Xiamen Tmax Battery Equipments Limited was set up as a manufacturer in 1995, dealing with lithium battery equipments, technology, etc. We have total manufacturing facilities of around 200000 square foot and more than 230 staff. Owning a group of experie-nced engineers and staffs, we can bring you not only reliable products and technology, but also excellent services and real value you will expect and enjoy.
A battery fabrication machine is a specialized piece of equipment designed to handle one or more stages in the production of batteries. These machines are integral components of battery fabrication lines, enabling the precise and efficient manufacturing of individual cells, modules, or complete battery packs. Each machine is tailored to perform specific tasks, ensuring highquality and consistent battery production.
In this article, we will explore the types, functionalities, advantages, challenges, and innovations driving the evolution of battery fabrication machines.
●Types of Battery Fabrication Machines
Battery fabrication machines can be categorized based on the stage of the manufacturing process they serve:
1. Material Preparation Machines
Function: Prepares raw materials such as active materials, binders, conductive additives, and current collectors.
Examples:
Mixing machines for creating slurries.
Dispensing systems for applying materials.
2. Coating and Drying Machines
Function: Applies active material slurries onto current collector foils (aluminum for cathodes, copper for anodes) and dries them.
Examples:
Slotdie coating machines.
Controlled drying ovens.
3. Calendering Machines
Function: Compacts coated electrodes to achieve desired density and porosity.
Examples:
Rolltoroll calendering systems.
4. Cutting and Slitting Machines
Function: Cuts or slits coated electrodes into precise dimensions.
Examples:
Laser cutting machines.
Precision slitting systems.
5. Stacking/Winding Machines
Function: Assembles electrodes and separators into stacked or wound configurations.
Examples:
Stacking machines for prismatic and pouch cells.
Winding machines for cylindrical cells.
6. Cell Assembly Machines
Function: Integrates electrodes, separators, electrolytes, and casing into complete battery cells.
Examples:
Electrode insertion systems.
Sealing and welding equipment.
7. Electrolyte Filling Machines
Function: Injects electrolytes into assembled cells under controlled conditions.
Examples:
Vacuum filling systems.
Pressure control units.
8. Formation and Aging Machines
Function: Activates and stabilizes battery cells through controlled charging and discharging cycles.
Examples:
Formation chambers with temperature control.
Aging racks.
9. Testing and Sorting Machines
Function: Evaluates cell performance and sorts them based on capacity, internal resistance, and other parameters.
Examples:
Testing stations with advanced sensors.
Automated sorting systems.
10. Module/Pack Assembly Machines
Function: Combines individual cells into modules or packs for enduse applications.
Examples:
Welding systems for interconnects.
Encapsulation and packaging equipment.
●Functionalities of Battery Fabrication Machines
1. Automation:
Reduces human intervention, minimizes errors, and increases throughput.
2. Precision Control:
Ensures uniformity in thickness, density, alignment, and electrical connections.
3. RealTime Monitoring:
Continuously measures and adjusts variables like temperature, pressure, and speed during production.
4. Scalability:
Adaptable to different battery chemistries, sizes, and form factors (cylindrical, prismatic, pouch).
5. Integration:
Connects seamlessly with other machines in the fabrication line for optimized efficiency.
1. High Throughput:
Enables mass production of batteries with consistent quality.
2. Cost Efficiency:
Minimizes labor costs and material waste through automation.
3. Improved Performance:
Ensures optimal alignment and contact between components for better battery performance.
4. Environmental Benefits:
Dry electrode processes and ecofriendly practices reduce solvent use and waste.
5. Customization:
Can be tailored to handle specific materials and chemistries, including emerging technologies like solidstate batteries.
●Challenges in Battery Fabrication Machines
1. Complex Material Handling:
Delicate materials like solidstate electrolytes require specialized handling to avoid damage.
2. Uniformity Control:
Achieving consistent quality across large batches is challenging.
3. Binder Selection:
Developing binders that work effectively in dry conditions while maintaining adhesion is complex.
4. High Initial Costs:
Advanced machinery and specialized components come with significant upfront investment.
5. Process Optimization:
Finetuning parameters such as temperature, pressure, and speed is essential for achieving consistent results.
●Innovations in Battery Fabrication Machines
To address these challenges and enhance productivity, manufacturers are incorporating cuttingedge technologies:
1. AI and Machine Learning:
Predictive analytics optimize machine performance, detect anomalies, and improve yield rates.
2. RealTime Monitoring Systems:
Integrated sensors and vision systems provide continuous feedback on critical parameters.
3. Modular Design:
Flexible systems allow for easy reconfiguration to test new materials and chemistries.
4. Sustainability Features:
Ecofriendly practices and recycling capabilities minimize waste and energy consumption.
5. Integration with Automation:
Collaborative robots (cobots) and IoTenabled systems enhance efficiency and reduce human intervention.
●Applications of Battery Fabrication Machines
Battery fabrication machines are used in various industries, including:
1. Electric Vehicles (EVs):
Produces highcapacity, longlife batteries for EVs.
2. Consumer Electronics:
Manufactures compact and efficient batteries for smartphones, wearables, and portable devices.
3. Renewable Energy:
Develops durable batteries for gridscale energy storage systems.
4. Industrial Applications:
Creates highperformance batteries for heavyduty applications like trucks, buses, and construction equipment.
●The Future of Battery Fabrication Machines
As the demand for sustainable and highperformance energy storage solutions grows, battery fabrication machines will continue to evolve. Key trends shaping the future include:
1. Increased Automation:
Fully autonomous systems will further boost production speeds and reduce costs.
2. Customization Options:
Modular designs will enable manufacturers to tailor machines for specific materials and cell designs.
3. Focus on Sustainability:
Ecofriendly practices and recycling capabilities will become integral parts of future systems.
4. Integration with Emerging Technologies:
Solidstate batteries, flexible electronics, and autonomous systems will drive new innovations in machine design.
5. Smart Manufacturing:
IoTenabled systems will leverage big data and AI to optimize production, reduce waste, and enhance efficiency.
●Conclusion
Battery fabrication machines are the heart of modern battery manufacturing, enabling the development of highperformance, costeffective, and sustainable batteries. Their ability to handle diverse materials, optimize processes, and scale production makes them indispensable for meeting the growing global demand for energy storage solutions.
What excites you most about the role of battery fabrication machines in driving innovation and sustainability in the energy storage sector? Share your thoughts below! Together, let’s explore how this technology can shape the future of energy storage.
 English▼
English▼





 +86 13174506016
+86 13174506016 David@tmaxcn.com
David@tmaxcn.com

